貨號
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN40886R-100ul
100ul
¥2470.00
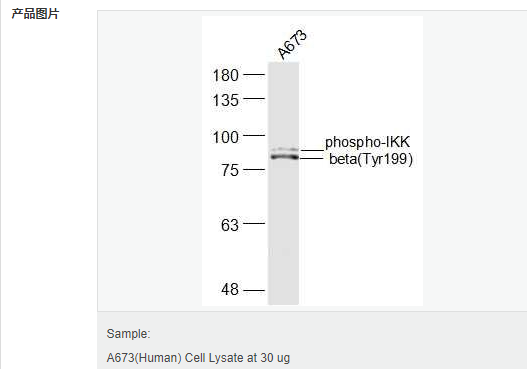
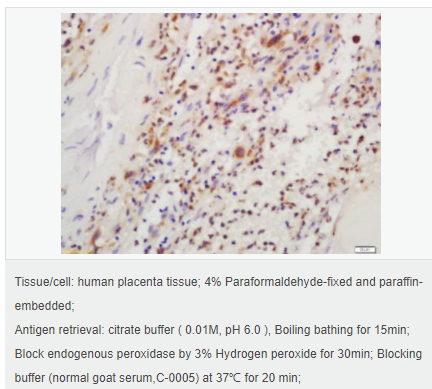
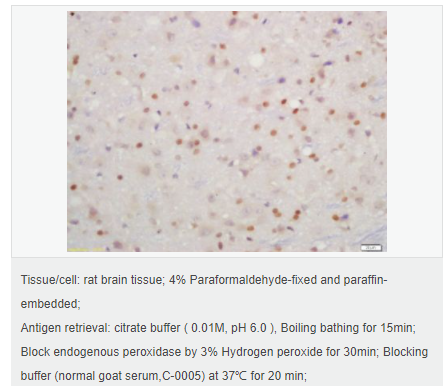
交叉反應(yīng):Rat,Human(predicted:Rabbit,Horse,Pig,Dog,Mouse) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | phospho-IKK beta (Tyr199) |
| 中文名稱 | 磷酸化KB抑制蛋白激酶β抗體 |
| 別 名 | IKK beta (phospho Y199); IKK beta (phospho Tyr199); p-IKK beta (Tyr199); IKKI kappa B kinase 2; IKKβ; IKK β; I kappa B kinase beta; IkBKB; IKK 2; IKK B; IKK2; IKKB; Inhibitor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells kinase beta; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase beta subunit; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit beta; MGC131801; NFKBIKB; Nuclear factor NF kappa B inhibitor kinase beta; Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor; IKKB_HUMAN. |
| 產(chǎn)品類型 | 磷酸化抗體 |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 腫瘤 免疫學(xué) 信號轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo) 轉(zhuǎn)錄調(diào)節(jié)因子 激酶和磷酸酶 細(xì)胞粘附分子 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, Rat, (predicted: Mouse, Dog, Pig, Horse, Rabbit, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 87kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞核 細(xì)胞漿 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human IKK beta around the phosphorylation site of Tyr199:QK(p-Y)TV |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | IKK beta (I-Kappa-B kinase-beta) is a member of the IKK complex which is composed of IKK alpha, IKK beta, IKK gamma and IKAP. Phosphorylation of I-Kappa-B on a serine residue by the IKK complex frees NF-kB from I-Kappa-B and marks it for degradation via ubiquination. IKK beta has been shown to activate NF-kB and phosphorylate IKB alpha and beta. Phosphorylation of 2 sites at the activation loop of IKK beta is essential for activation of IKK by TNF and IL1. Once activated, IKK beta autophosphorylates which in turn decreases IKK activity and prevents prolonged activation of the inflammatory response. Additionally, IKK beta activity can also be regulated by MEKK1. Function: Serine kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway which is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses. Acts as part of the canonical IKK complex in the conventional pathway of NF-kappa-B activation and phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B on 2 critical serine residues. These modifications allow polyubiquitination of the inhibitors and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In turn, free NF-kappa-B is translocated into the nucleus and activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis. In addition to the NF-kappa-B inhibitors, phosphorylates several other components of the signaling pathway including NEMO/IKBKG, NF-kappa-B subunits RELA and NFKB1, as well as IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE. IKK-related kinase phosphorylations may prevent the overproduction of inflammatory mediators since they exert a negative regulation on canonical IKKs. Also phosphorylates other substrates including NCOA3, BCL10 and IRS1. Within the nucleus, acts as an adapter protein for NFKBIA degradation in UV-induced NF-kappa-B activation. Subunit: Component of the I-kappa-B-kinase (IKK) core complex consisting of CHUK, IKBKB and IKBKG; probably four alpha/CHUK-beta/IKBKB dimers are associated with four gamma/IKBKG subunits. The IKK core complex seems to associate with regulatory or adapter proteins to form a IKK-signalosome holo-complex. The IKK complex associates with TERF2IP/RAP1, leading to promote IKK-mediated phosphorylation of RELA/p65. Part of a complex composed of NCOA2, NCOA3, CHUK/IKKA, IKBKB, IKBKG and CREBBP. Part of a 70-90 kDa complex at least consisting of CHUK/IKKA, IKBKB, NFKBIA, RELA, IKBKAP and MAP3K14. Found in a membrane raft complex, at least composed of BCL10, CARD11, DPP4 and IKBKB. Interacts with SQSTM1 through PRKCZ or PRKCI. Forms an NGF-induced complex with IKBKB, PRKCI and TRAF6. May interact with MAVS/IPS1. Interacts with NALP2. Interacts with TICAM1. Interacts with Yersinia yopJ. Interacts with FAF1; the interaction disrupts the IKK complex formation. Interacts with ATM. Part of a ternary complex consisting of TANK, IKBKB and IKBKG. Interacts with NIBP; the interaction is direct. Interacts with ARRB1 and ARRB2. Interacts with TRIM21. Interacts with NLRC5; prevents IKBKB phosphorylation and kinase activity. Interacts with PDPK1. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Membrane raft. Note=Colocalized with DPP4 in membrane rafts. Tissue Specificity: Highly expressed in heart, placenta, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, spleen, thymus, prostate, testis and peripheral blood. Post-translational modifications: Upon cytokine stimulation, phosphorylated on Ser-177 and Ser-181 by MEKK1 and/or MAP3K14/NIK as well as TBK1 and PRKCZ; which enhances activity. Once activated, autophosphorylates on the C-terminal serine cluster; which decreases activity and prevents prolonged activation of the inflammatory response. Phosphorylated by the IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE, which is associated with reduced CHUK/IKKA and IKBKB activity and NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription. Acetylation of Thr-180 by Yersinia yopJ prevents phosphorylation and activation, thus blocking the I-kappa-B pathway. Ubiquitinated. Monoubiquitination involves TRIM21 that leads to inhibition of Tax-induced NF-kappa-B signaling. According to PubMed:19675099, 'Ser-163' does not serve as a monoubiquitination site. According to PubMed:16267042, ubiquitination on 'Ser-163' modulates phosphorylation on C-terminal serine residues. Monoubiquitination by TRIM21 is disrupted by Yersinia yopJ. Similarity: Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. I-kappa-B kinase subfamily. Contains 1 protein kinase domain. SWISS: O14920 Gene ID: 3551 Database links: Entrez Gene: 3551 Human Entrez Gene: 16150 Mouse Omim: 603258 Human SwissProt: O14920 Human SwissProt: O88351 Mouse Unigene: 597664 Human Unigene: 277886 Mouse Unigene: 19222 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |